Experiment No :2
Aim: To measure the i)Thickness of the Glass Plate ii) Diameter of the metal wire iii) Volume of the given Glass Plate.
Apparatus : Screw Gauge , Glass Plate and Metal wire .
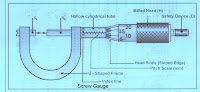
Description : Screw Gauge consists of U shaped metallic frame.To one side of this U frame a long hallow cylindrical tube with a nut inside it, the inner side of cylindrical nut contains a uniform thread cut in it.On the other side of U frame a fixed stud with a plane face is attached.
A screw is fitted in the cylindrical nut.One side of the screw
has a plane face similar to that of stud
. The faces of
and
are plane and parallel to one another. The other end of the screw
carries a milled head ‘H’ attached to a cap ‘C’ with a sloping edge. When the head H is rotated, the screw moves ”to and fro” in the nut.The milled head H is provided with a safety device ‘D’ to rotate the head H.When the object is held between the stud
and screw
and the head H is rotated using the safety device (D), it produces crackling sound when optimum pressure is applied on the object.
The outer surface of long cylindrical nut consists of a thick horizontal line ‘P’ parallel to the axis of cylindrical tube.This line ‘P’ is called Index line. Along the index line a scale is graduated in millimeters.This scale is called Pitch Scale.On the sloping edge of the cap ‘C’ a circular scale is graduated, which consists of 100 equal divisions, this scale is called Head scale.
Theory : The screw gauge works on the principle of screw.
When we rotate the head ‘H’ by means of safety device ‘D’ through one complete rotation, the distance moved by the screw for every complete rotation is constant. This constant distance moved by the screw for one complete rotation of head ‘ H ‘ is called Pitch of the screw.If the head scale has 100 equal divisions, then the distance moved by the screw for even 1/100 of a complete rotation can be measured accurately,this is called Least count of screw gauge.
Therefore Least count (L.C) = .
Procedure :First we have to determine the least count of the given Screw gauge.
To determine the least count of the screw gauge, the head ‘H’ is rotated through certain (say 5) number of complete rotations.The distance moved by the sloped edge over the pitch scale is measured.
Now substitute these values in the formula of pitch of the screw = .
Least count L.C = .
Now check whether the given screw gauge has any ZERO ERROR or not. To determine the ZERO ERROR, the head H is rotated until the flat end of the screw touches the plane surface of the stud
(do not apply excess pressure) i.e we have to rotate the head only by means of safety device ‘D’ only.
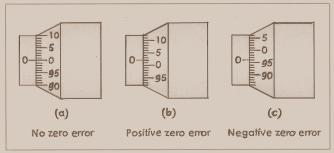
When and
are in contact,the zero of the head scale perfectly coincides with the index line as in Fig-(a). In such case there will be no ZERO ERROR and no correction is required.
When and
are in contact,the zero of the head scale is below the index line as in Fig(b), such ZERO ERROR is called positive ZERO ERROR, and the correction is negative.
When and
are in contact,the zero of the head scale is above the index line as in Fig(c) , such ZERO ERROR is called negative ZERO ERROR, and the correction is positive.
a) Determine the thickness of glass plate : The given object glass plate is held between the two parallel surfaces of fix stud and screw tip
. Note the completed number of divisions on pitch scale, which is called PITCH SCALE READING (P.S.R). The number of the head scale division coinciding with the index line is noted, which is called OBSERVED HEAD SCALE READING n’. If the given screw gauge has ZERO ERROR (x) the correction is made by adding or subtracting the ZERO ERROR (x) from the OBSERVED HEAD SCALE READING n’.The corrected value (n’-x) or (n’+x) is called the HEAD SCALE READING (H.S.R) n.
To calculate the fraction the H.S.R (n) is multiplied by the least count (L.C).
Thickness of the Glass plate = Total reading = P.S.R + - - - - - (1)
Changing the position of glass plate , 5 readings should be taken, and recorded in the table-1. Every time calculate the total thickness of the glass plate using equation (1).
Average of the 5 readings of the glass plate should be calculated, to get the average thickness(t) of the given glass plate.
b) Determine the radius(r) of the given metal wire :The given object metal wire is held between the two parallel surfaces of fix stud and screw tip
. Note the completed number of divisions on pitch scale, which is called PITCH SCALE READING (P.S.R). The number of the head scale division coinciding with the index line is noted, which is called OBSERVED HEAD SCALE READING n’. If the given screw gauge has ZERO ERROR (x) the correction is made by adding or subtracting the ZERO ERROR (x) from the OBSERVED HEAD SCALE READING n’.The corrected value (n’-x) or (n’+x) is called the HEAD SCALE READING (H.S.R) n.
To calculate the fraction the H.S.R (n) is multiplied by the least count (L.C).
Diameter of the given metal wire = Total reading = P.S.R +
Changing the position of metal wire, 5 readings should be taken, and recorded in the table-2. Every time calculate the total diameter (d) of the metal wire using equation (1).
Average of the 5 diameter of the metal wire should be calculated, to get the average diameter(d) of the given metal wire.
Radius (r) of the metal wire = mm.
Precautions : i ) Pitch scale reading (P.S.R) should be taken carefully without parallax error ii ) Head scale reading (H.S.R) should be taken carefully without parallax error iii )Screw must be rotated by holding the safety device ‘D’ iv ) Do not apply excess pressure on the object held between the surfaces and
.
v ) The screw is rotated in only one direction either clock wise or anti-clock wise to avoid the back lash error.
Observations : i ) Zero error =
ii) Zero correction = ...... mm
iii ) Distance moved by the head for 5 complete revolutions = mm
iv ) Number of head scale divisions =
v) Pitch of the screw =
vi) Least count (L.C) =
.
Table -1 ( Thickness of glass plate ) :
S.No
Pitch Scale Reading (P.S.R) amm
Observed H.S.R (n’)
Correction (x)
Corrected H.S.R n=n’-x
Fraction b=n*L.C
Total reading (a+b) mm
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Average thickness of the glass plate (t) = ..... mm
Table - 2 (Diameter of the metal wire):
S.No
Pitch Scale Reading (P.S.R) amm
Observed H.S.R (n’)
Correction (x)
Corrected H.S.R n=n’-x
Fraction b=n*L.C
Total reading (a+b) mm
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Average diameter d = .... mm
Average radius r = = .... mm .
c ) Volume of Glass plate (v) : The length ( l ) , breadth ( b) are determined using vernier calipers and thickness ( t ) of the glass plate is determined using screw gauge. The values of l ,b and t are substituted in the equation of volume V = ( l )( b )( t )